√ダウンロード (x-y-2)dx (x-2y-3)dy=0 338672-7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0
Solve The Differential Equation Xy 2 X Dx X 2y Y Dy 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
2y)dx (x?y3 – x)dy = 0 3 by multiplying by the integrating factor An implicit solution in the form F (x,y)=C is = C, where is an arbitrary constant, and (Type an expression using x and y as the variables) Previous questionX 2ydx−(x 3y 3)dy=0 dydx = x 2yx 3y 3 Putting x=vydydx =vy dydv dydx = x 2yx 3y 3 ⇒vy dydv = v 2y 3v 3y 3y 3 = v 2v 31 y dydv = v 2v 31 −v= v 2v 31−v 3 = v 21 ⇒v 2dv= ydy (variable separable method)Integrating both sides∫v 2dv=∫ ydy
7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0
7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0-Y = 3x2 3x – 1 х — у— In(x 2у 1) %3D С O D x²Transcribed image text Solve the equation (3x?

Ordinary Differential Equations 3y 2 X b Dx 2y Y 2 3 b Dy 0 Admits An Integrating Factor Which Is A Function Of X Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
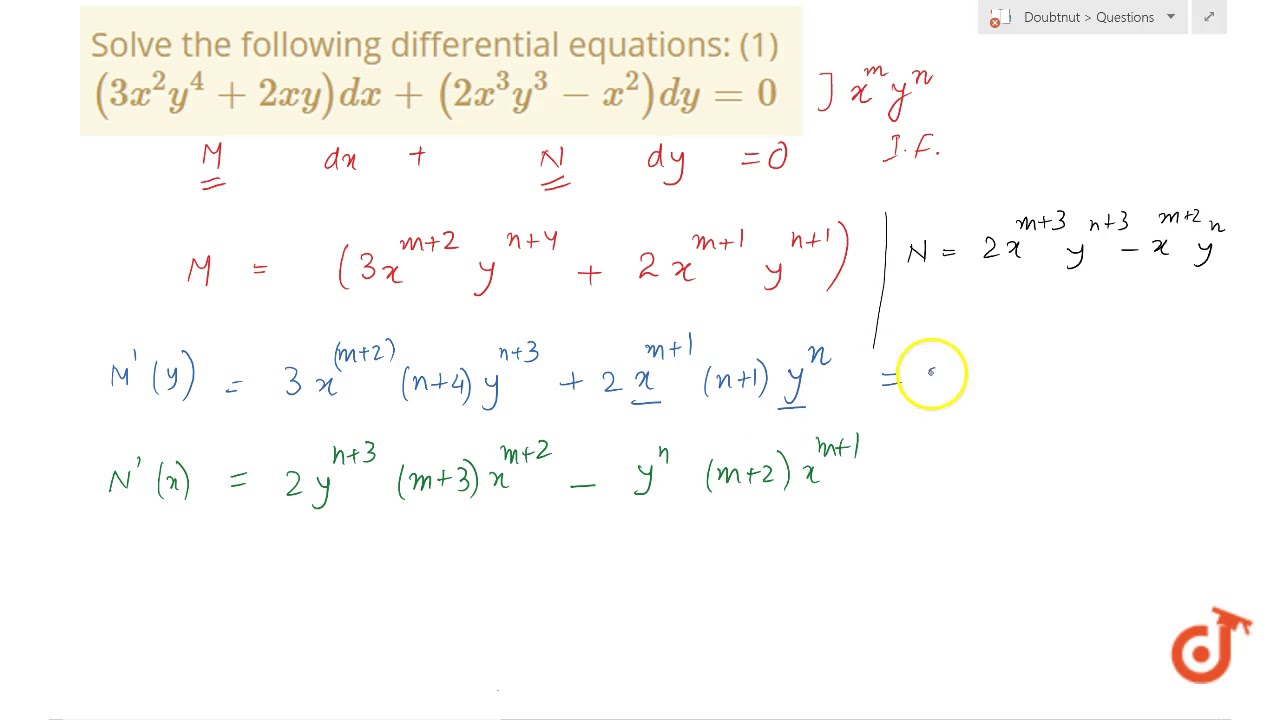
See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading By Integrating Factors y (2x – y 1)dx x (3x – 4y 3)dy = 0 (x 2 y 2 1)dx x (x – 2y)dy = 0 (4xy 3y 2 – x)dx x (x 2y)dy = 0 y (x y 1)dx x (x 3y 2)dy = 0 y 2 dx (3xy y 2 –Y = 3 when x = 0 dy dx = −2y separate variables and integrate ∫ dy y = − ∫2dx ⇒ lny c = −2x let lc = lnk we have therefore lny lnk = −2x ⇒ lnky = − 2xTake xy = V (x) , so dy = ( xdV Vdx )/x^2After some manipulations one obtains (3V^3)dx/x V (V 1 )dV =0 ,which is separated as follows dx/x = V (V1)dV/3V^3 Integrating yields 3ln (Cx) = lnV 1/V The solution of the equation is obtained as y = K (x^2)e^ (1/xy) , where K = C^3 18K views
Find the particular solution of the following differential equation (x 2y^2) dy/dx = y, when x = 2, y = 1 asked in Differential Equations by Amayra ( 314k points) differential equationsFinalize answer free of Logarithms and fractions Express final answer in its simplest form (x 2y 3)dx (4x y 3)dy = 0 sin y (x sin y)dx 2x^2 cosydy = 0Here is another way y ( y 2 x 2) d x x ( 2 x 2 − y) d y = 0 Substitute y = t x t ( t 2 x) = ( t − 2 x) y ′ Note that y ′ = t ′ x t t ( t 2 x) = ( t − 2 x) ( t ′ x t) After some simplifications you get t ′ ( t − 2 x) = 4 t Consider now x ′ = d x d t
7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | 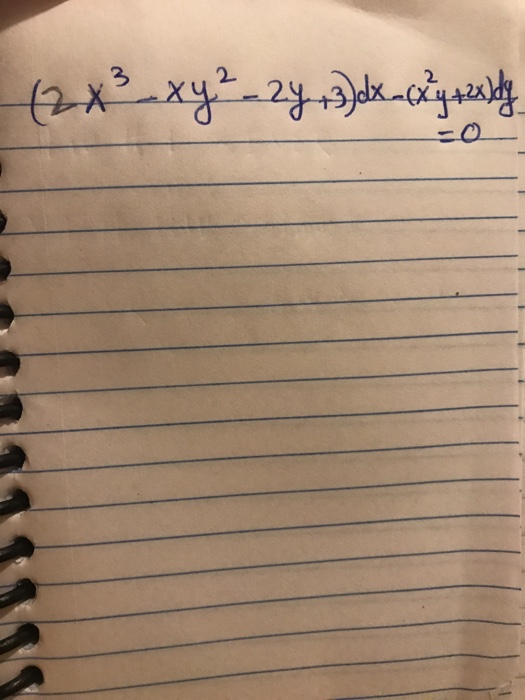 | |
 |  | |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 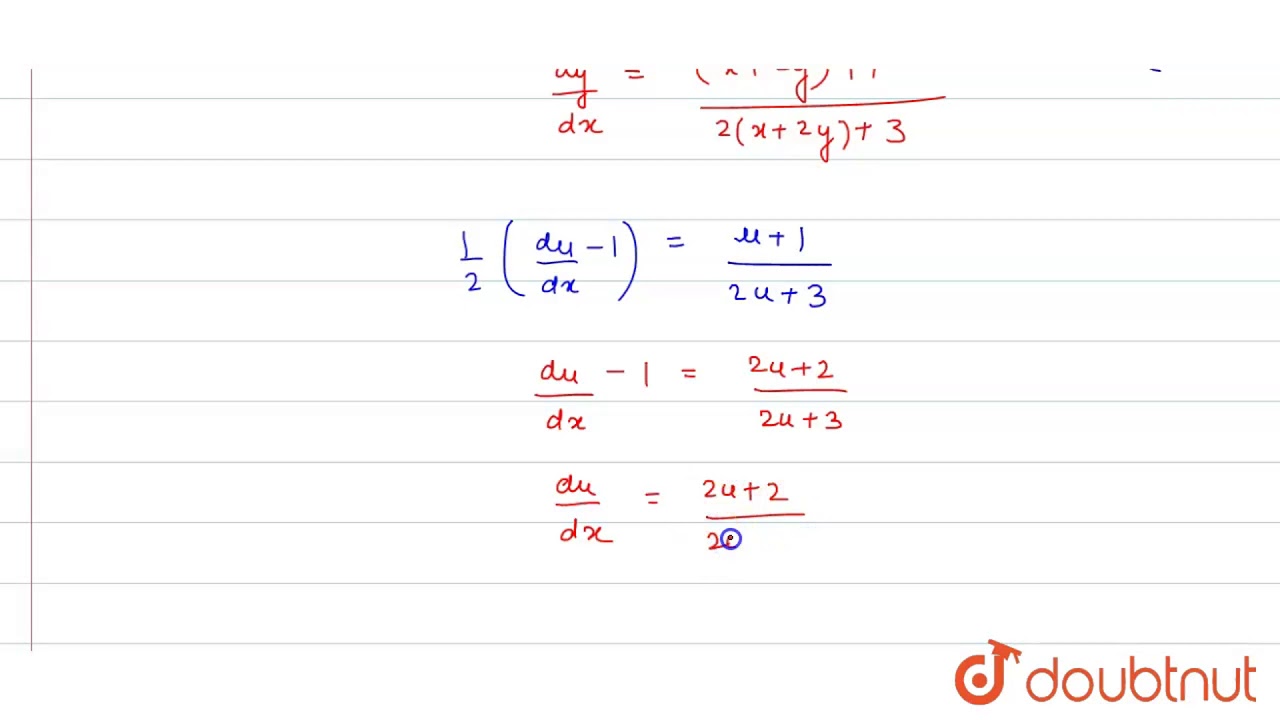 | 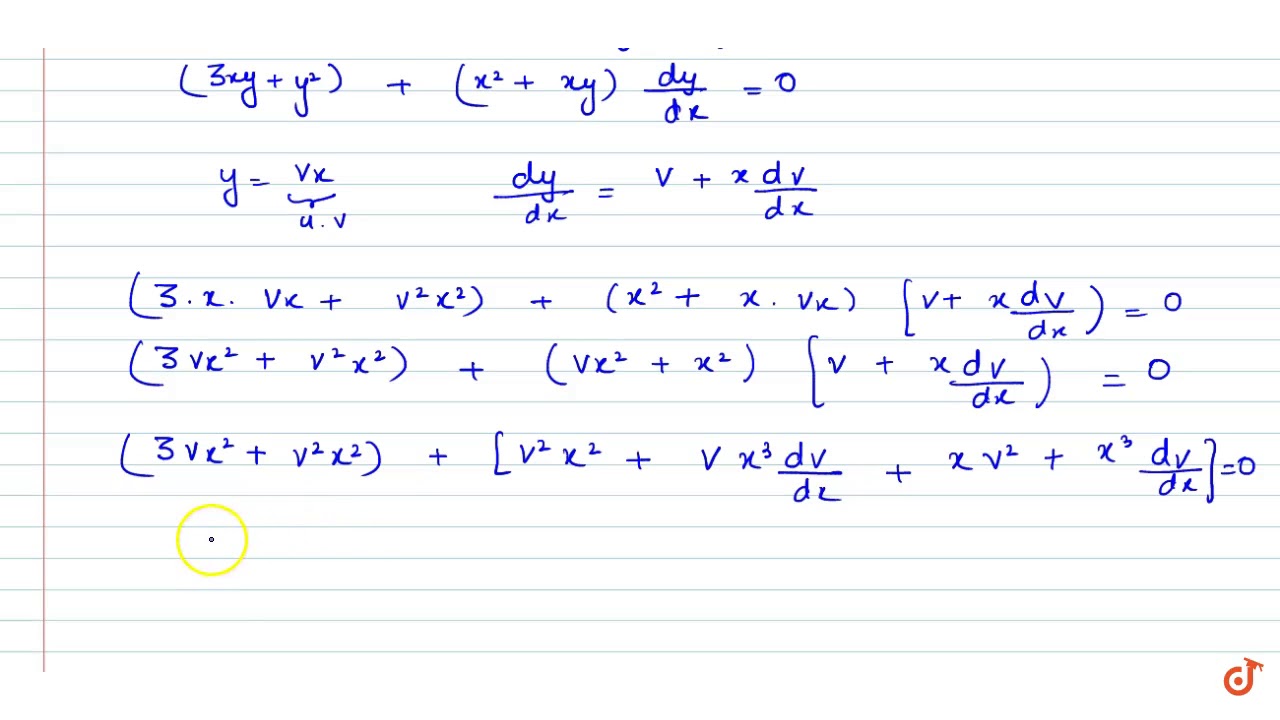 |
 |  | 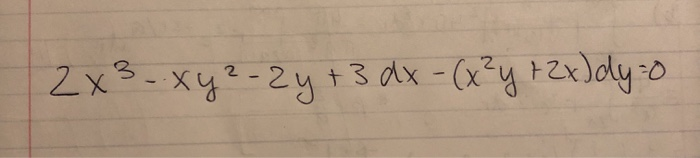 |
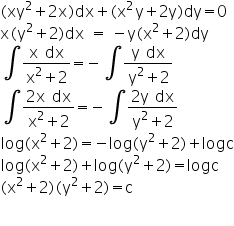 | ||
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 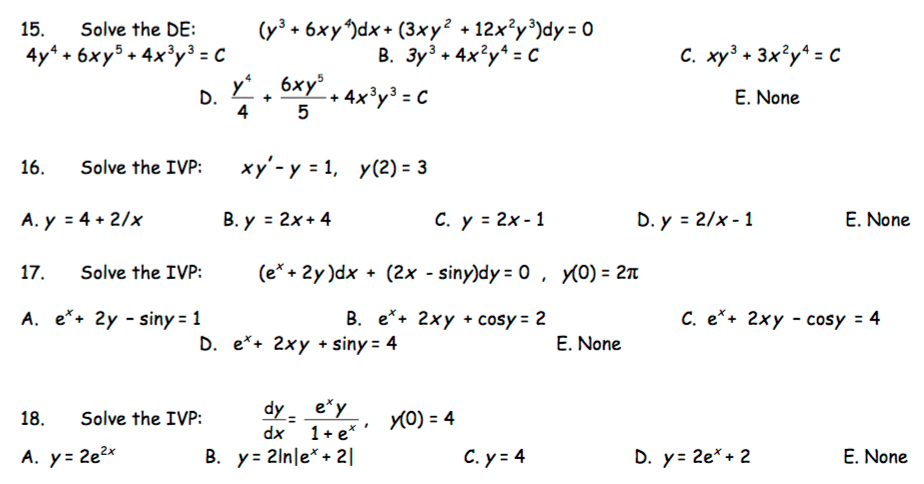 | |
 |  | |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  | |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
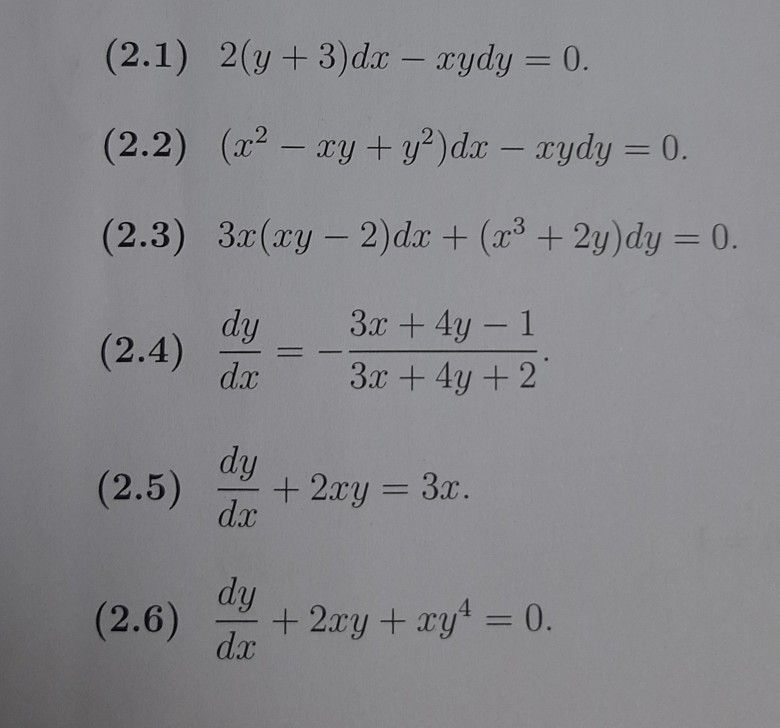 |  | |
「7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
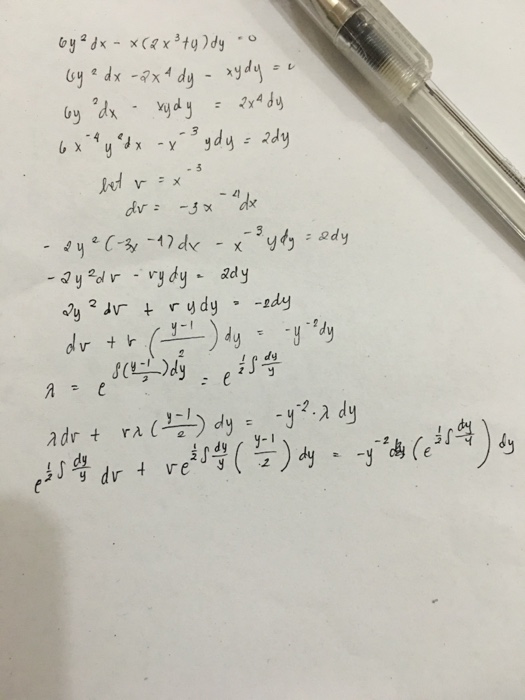 |  |  |
 |
To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 3 To multiply powers of the same base, add their exponents Add 2 and 1 to get 3 \left (x^ {3}y^ {2}\right)dx3xy^ {3}d=0 ( x 3 y 2) d x − 3 x y 3 d = 0 Use the distributive property to multiply x^ {3}y^ {2} by d//mathstackexchangecom/questions//whatdoesdydxy2x2xymodel There are probably many different things that are modeled by those equations Rewrite the first equation as (xy)dy (y^2x^2)dx=0 (xy)dy (x^2y^2)dx=0 Can be represented as the product of a
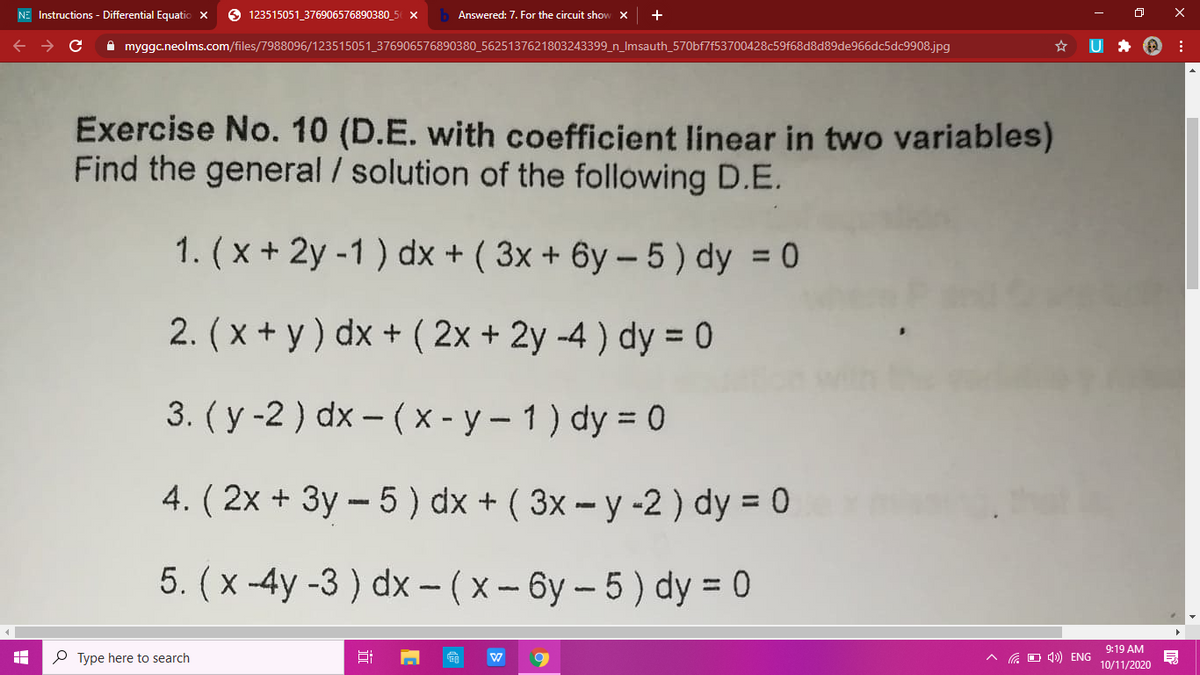
Incoming Term: (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0, 7. (x-y-2)dx+(x-2y-3)dy=0, (x^3+xy^2)dx+(x^2y+y^3)dy=0, (x-y-2)dx-(2x-2y-3)dy=0, solve (x^3+xy^2)dx+(x^2y+y^3)dy=0, 3x(xy-2)dx+(x^3+2y)dy=0, (y^2-3y-x)dx+(2y-3)dy=0, x^2 y dx-(x^3+y^3)dy=0, (x^(2)y-2xy^(2))dx-(x^(3)-3x^(2)y)dy=0, (x^(2)y-2xy^(2))dx-(x^(3)-2x^(2)y)dy=0,
コメント
コメントを投稿